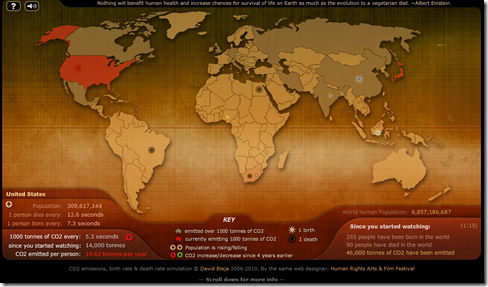
Both theories relate food supply with population size, based on the agricultural methods used for food production.
Malthus Theory:
- Published in “The Principle of Population” in 1798
- It presents an approach focusing in the population size being determined by the availability of food
- Population growth follows a geometric progression and food growth follows an arithmetic one.
- When food supply is scarce, population size will adjust to it.
- Food production incensement is a slow and difficult process.
- It states that controlling population growth is easier than increasing the food supply.
- The theory doesn’t present the possibility of controlling the human birth rate, but establishes a extremely pessimistic approach where organisms of the human population will just die until food supply is enough.
- It doesn’t consider all of the changes that the industrial revolution brought.
Boserup Theory:
- Presents a model of population in which the size determines the amount of food available.
- When there’s stress in relation between food supply and population size, people will always find a way to increase production.
- Workforce, machinery and fertilizers are the methods applied to increase food production.
Limitations:
- At first, when population is low, lands are used intermittently, using fallowing (the burning of crops) to make lands more fertile. It is when population increases, that lands are used in a scheduled way. However, this requires more effort in maintaining the land.
- The more maintenance, the more agricultural innovation, but labor increases towards farmers.
- This tends to increase workforce but decrease crop efficiency, a process Ester calls ‘agricultural intensification’.